Insecure third-party connections to your GitHub may trigger a supply chain attack

Do you really know how many third-party applications have access to your GitHub repository?
IT teams, DevOps, and developers are increasingly authorizing new third-party applications to access the organization’s GitHub repositories in a bid to boost productivity. However, many of these are shadow integrations (connected via API keys, service accounts, webhooks, OAuth tokens, or even SSH keys) that are not vetted by security teams. They are also often over-privileged or were connected by users who have since left the company.
These unmonitored connections to your GitHub (of which there could be thousands) create a new ecosystem of supply chain dependencies that expand your attack surface and expose your organization to supply chain attacks, compliance violations, and unauthorized access.
Organizations should protect their API keys as vigorously as they protect their passwords. Leaking an API key can be more consequential than leaking a username and password login since logins are often protected by two-factor authentication nowadays, whereas API keys are not.
The threat is real: GitHub attacks triggered by third-party integrations
Recent high-profile attacks targeting Github or services that are connected to GitHub environments, reveal a new generation of supply chain attacks, in which attackers take advantage of access granted to third-party cloud services as a backdoor into GitHub repositories.
- GitHub Dependabot (September 2023): Hackers stole GitHub Personal Access Tokens (PAT). These tokens were then used to make unauthorized commits as Dependabot to both public and private GitHub repositories.
- CircleCI (January 2023): An employees’ computer that was compromised by malware, allowed threat actors to access and steal CircleCI session tokens, which allow the same access as the account owner even when the accounts are protected with MFA. Since the engineering employee had privileges to generate production access tokens as part of their regular duties, the threat actors were able to escalate privileges to access and exfiltrate data from customer environment variables, tokens, and keys – all without CircleCI’s knowledge.
- Slack GitHub Repositories (January 2023): In this incident, threat actors gained access to Slack’s externally hosted GitHub repositories via a “limited” number of stolen Slack employee tokens. From there, they were able to download private code repositories
GitHub integration risks found in real organizations’ engineering environments
From our research among organizations of over 1,000 employees, we discovered GitHub environments have:
- Thousands of connections to third-party applications and cloud services
- The majority of connections are shadow connections, connected with API keys, Webhooks and even SSH keys (in comparison to only dozens of integrations to GitHub apps)
- On average, 4-5 new integrations are added on a weekly basis
As a result, there is simply too much data for security teams to review to ensure that all GitHub integrations are secure. And while the GitHub admin console tracks access credentials and GitHub app integrations, it doesn’t see and track the majority of the integrations – the ‘unstructured’ integrations (connected via API keys and SSH keys), nor does it provide visibility into who created the integrations, or who is the vendor behind each app. Therefore, it cannot detect threats posed by untrusted or insecure configurations, apps, or integrations.
Using the Astrix Security platform, our customers discovered that their GitHub environment is far more exposed to third-party cloud services than they thought, with the average number of connections 10x more than the estimated number. The troubling findings include:
- Redundant access: 33% of the active access tokens connecting GitHub and third-party apps are unused.
- Over-privileged access: Connections with common cloud services (Heroku, Codecov, Travis CI, etc) were configured with admin permissions.
- Dangerous practices: 74% of Personal Access Tokens in GitHub environments have no expiration, and 59% of the webhooks in GitHub are misconfigured – meaning they are unencrypted and unassigned.
- Untrusted vendors: 50% of the apps connected to GitHub environments are non-marketplace apps – meaning they were not vetted by an official app store.
How to ensure your GitHub is securely connected to cloud services with Astrix
Astrix Security Platform allows GitHub users to be productive while also ensuring robust security by delivering:
- Holistic visibility: Astrix provides a consolidated, comprehensive view of all the internal and third-party integrations with your GitHub environment (repositories, workflows, and configurations). You get complete visibility into which external services can access your GitHub resources, as well as the level of access and permissions granted to each one.
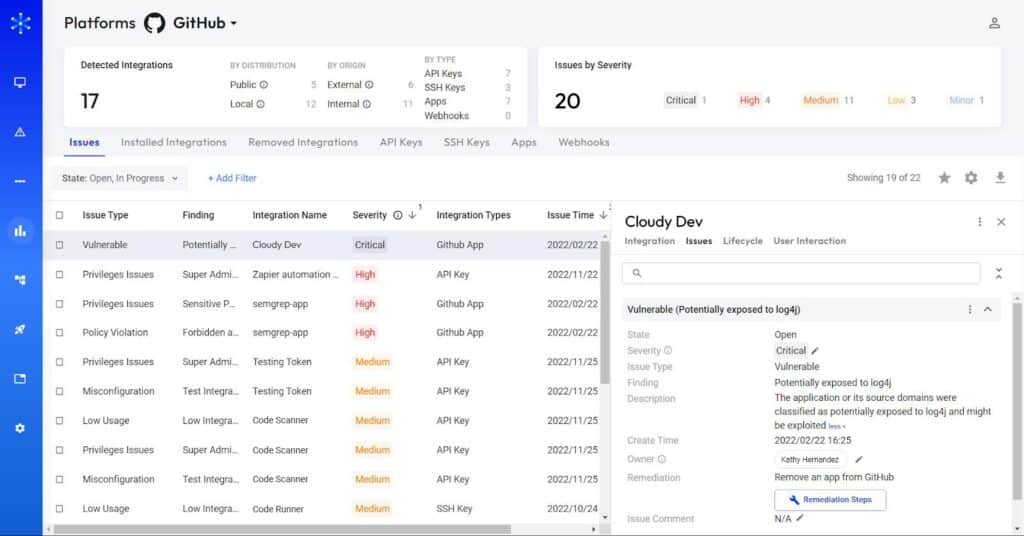
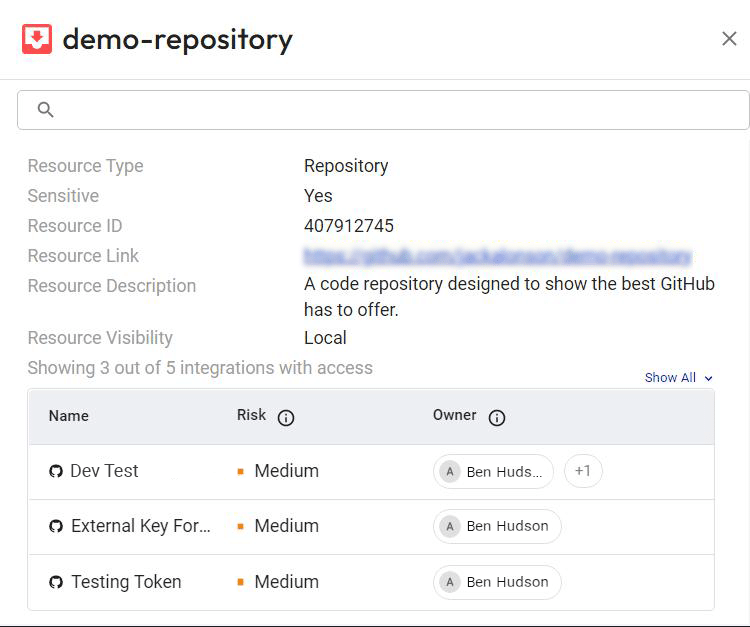
- Threat detection: Astrix automatically identifies malicious third-party integrations, anomalous behavior (like suspicious source IPs), overly permissive integrations, redundant applications, and insecure tokens. That means you know where GitHub risks lie and how they can be exploited.
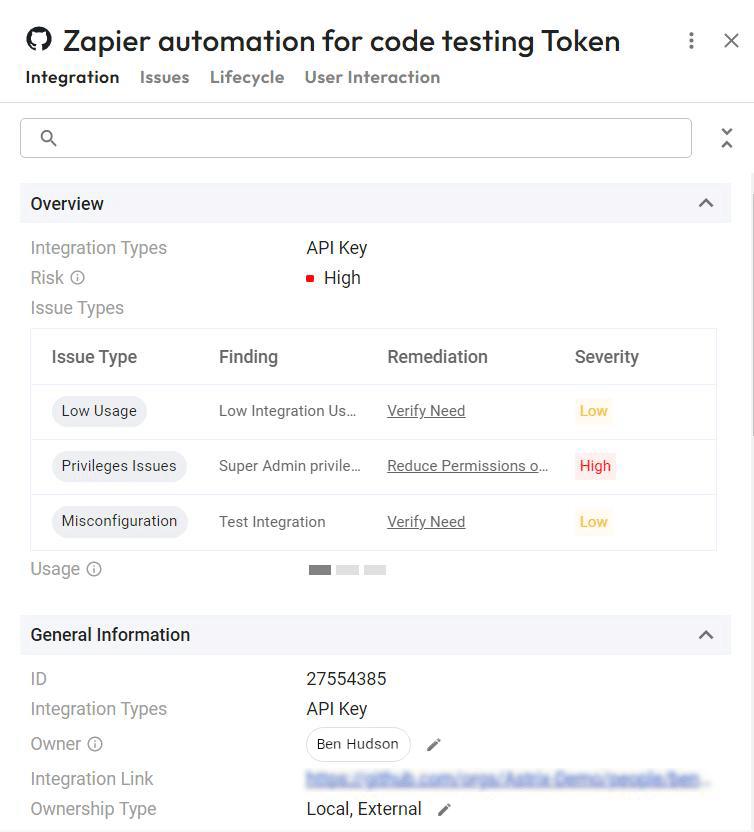
- Rapid remediation: By automating remediation workflows, integrating with your daily IT service management tools, and enabling end-users to resolve security issues in the process, Astrix can automatically remediate your GitHub security risks. This helps take the burden off of your IT team. Security admins Receive highly digested security alerts, including user feedback, threat context, severity level, and suggested remediation steps.
Learn more
Stay up-to-date with the latest in third-party integration threat prevention by downloading our free eBook, “The Ultimate Guide to Securing App-to-App Integrations.”
Or, contact us to discuss your business’s GitHub security risks and how Astrix can solve them.